Lithium batteries are an important part of productive life and are used in many applications, but it can be very frustrating when a lithium battery suddenly goes down, so you have to think about getting it back to normal quickly.
Lithium-ion batteries are still a relatively new technology compared to lead-acid batteries, so at BSLBATT we often come across dead or dormant lithium batteries due to customer mishandling, but with the right knowledge of lithium batteries and the correct procedures, you can bring your batteries back to life.
Read this article on why lithium batteries go down and how to get them back up, including the equipment needed and what to look for during operation.
About Lithium Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are the most popular and advanced battery technology available today, causing a reputation for high energy density, lightweight, and a long lifespan that can typically exceed 10 years for lithium batteries.
However, lithium-ion batteries are not complicated. Like traditional storage batteries, lithium-ion batteries are divided into a cathode, anode, diaphragm, and electrolyte, and rely on the movement of lithium ions between these components to function during charge and discharge cycles.
Currently, lithium batteries are widely used in electronic equipment, industrial vehicles, renewable energy and many other fields, learn more about BSLBATT lithium battery products.
Common Causes of Lithium-ion Battery Failure
We encountered customer feedback leading to the failure of lithium-ion batteries are usually categorized into the following 6 types of reasons:
Over-discharge
Over-discharge usually means that the battery power is discharged to a fairly low voltage level, for Li-ion batteries, this voltage level is usually around 2.5V. If the battery’s voltage drops to this level and remains at this voltage level for a long time, then this is considered to be an over-discharge of the battery.
Over-discharging impairs the battery’s ability to charge, and severe over-discharging may cause the battery to not be able to be recharged in addition to other problems such as internal short circuits or heat generation.
Overcharging
Every lithium battery has a designed upper voltage limit, usually 4.2V, once the voltage exceeds this limit, the positive electrode of the battery may absorb too many lithium ions, leading to electrode structure rupture, and internal side reactions may occur, leading to overheating, smoking or even explosion of the battery.
High Current Discharge
High current discharge may cause the internal temperature of the battery to rise rapidly, and the high temperature may damage the electrolyte inside the battery, causing the battery to short-circuit, and in severe cases, may even cause the battery to explode. In BSLBATT’s energy storage batteries, a discharge rate of 0.5C is usually recommended for use.
High-temperature Environment
For high-temperature environments, the chemical reaction inside the lithium battery will become more active, the electrolyte may be decomposed, generating a large amount of gas, or leading to the environmental dissolution of structural alloys, and the storage capacity of the battery will also be reduced, even if exposed to high temperatures for a short period, it may also significantly reduce the service life of the battery.
Natural Aging
In the process of charging and discharging lithium batteries, some lithium ions will penetrate into the electrodes, forming “dead lithium” that can not participate in the reaction, and can no longer be moved or release power, so that the effective capacity of the battery continues to decline.
Physical Pressure
The interaction between the positive and negative electrodes and electrolyte inside the battery requires a certain structural space, if pressed by external forces, it may lead to the rupture of this space, and the charging capacity of the battery will be affected, if the pressure is too great, the collision of the internal components of the battery may even puncture the diaphragm, causing the battery to short-circuit.
Manifestations of Lithium Battery Failure
If your lithium battery malfunctions or dies, it will usually manifest itself in the following ways:
- Sudden power loss
- Slow charging or no charging at all
- Higher battery temperatures
- Battery won’t turn on
- Battery bulging or any physical damage (such as rupture)
- Unusual noise
- Fast discharge rate
- Decreased cell consistency
- BMS shows poor battery data
What Equipment Do You Need to Wake up A Lithium Battery?
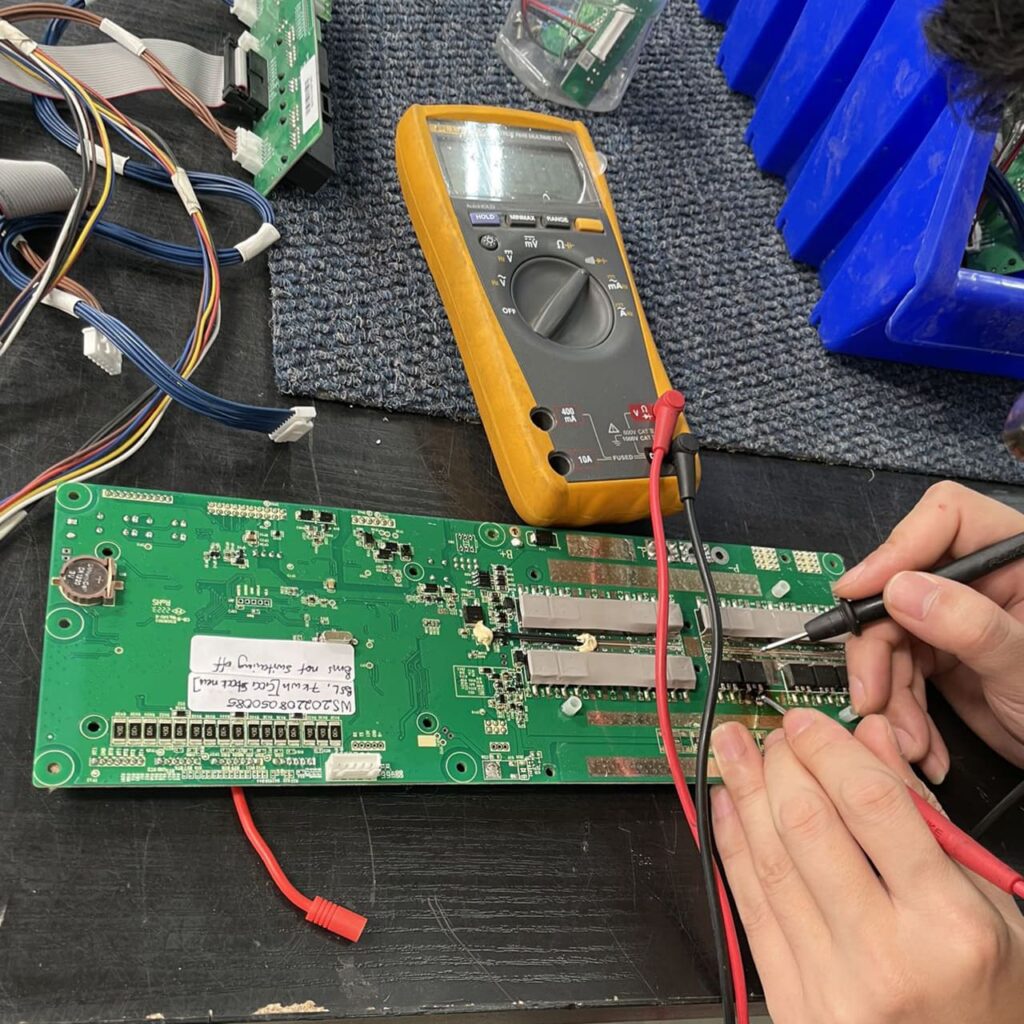

Multimeter for lithium battery
Lithium battery multimeter is an electronic instrument specialized in monitoring the status of lithium batteries. Through the digital display, the multimeter can conveniently show key parameters such as power, voltage, current and temperature, helping users to monitor the battery status in time and for safety monitoring. When servicing lithium batteries, it is recommended to use the meter for monitoring to ensure the safety and performance of the battery.
Compatible charger or power supply
Charger is also a necessary tool in lithium battery repair, but you must choose a charger that is compatible with the battery current and voltage used to charge the battery. It can intelligently charge the battery according to its type and capacity, ensuring that the battery will not be overcharged or over-discharged, prolonging the life of the battery.
Alligator clips or specialized jumper cables
Jumper cables are special wires mainly used to connect faulty lithium batteries to chargers or power supplies, and cables that match the battery cell voltage must be used during the repair process; alligator clips can be used to link the jumper cables securely to the positive and negative terminals of the batteries during the repair process, and they can also be connected to test equipment, chargers, and so forth, for troubleshooting or charging.
Battery booster sets
A battery booster pack is a power circuit component used to boost the DC voltage of a battery to a higher voltage. There are two things to keep in mind when using a battery booster pack:
- the output voltage should not exceed the maximum voltage that the lithium battery itself can accept
- The operating current should not exceed the maximum operating current that the battery can provide.
Protective equipment
- Gloves and goggles
Once the lithium battery short-circuits, it may explode, so in the maintenance of lithium batteries must wear gloves and goggles to protect personal safety. - Fire extinguisher
Lithium batteries may become unstable due to high temperatures, serious combustion and release of toxic gases, fire extinguishers are also very important equipment to prevent lithium batteries from catching fire.
How to Quickly Jumpstart a Dead Lithium-Ion Battery: A Step-by-Step Guide

Here are the steps you need to follow to quickly jumpstart a dead Lithium-Ion battery:
- Verify the appropriate charger
Initially, verify the compatibility and certification status of the charger you are using to make sure the voltage and current specifications match the battery. Prefer chargers from reputable manufacturers to ensure safety. - Connect the charger
Turn off power to devices with depleted batteries to minimize the possibility of electrical problems. Then connect the charger to the battery and power source, taking care to pair the positive and negative terminals correctly. - Voltage Confirmation
Use a multimeter to check the battery voltage to verify that it is within the acceptable range. If the voltage is too low, charging may fail or the battery may need to be replaced. - Alligator Clip Connection
Connect the red alligator clips to the positive terminal and the black ones to the negative terminal, paying attention to precise operation to prevent short circuits or damage to the battery and charger. - Charging process monitoring
Start the charger and monitor the charging status, noting any abnormal sounds, odors or overheating symptoms. It is important to maintain a safe charging environment. - Shutdown and Disconnection
When charging is complete, it is a priority to turn off the charger and disconnect the battery from the power source, following the manufacturer’s instructions to the letter. - Battery test
Wait for some time after charging before turning on the device. If it starts successfully, it can be plugged into your electrical equipment. If the battery successfully powers the device, congratulations! You have successfully started the depleted lithium-ion battery. If the device does not start properly or behaves abnormally, a more in-depth battery check or replacement may be required.
How to Avoid Your Lithium Battery Dying?
Avoid fully discharging the battery: Although lithium batteries can be 100% discharged, it will reduce the life of the battery or even cause irreversible damage, so you need to follow the manufacturer’s requirement to use the battery, for example, BSLBATT 51.2V lithium solar battery should be recharged in time when the voltage reaches 47V. And the maximum depth of discharge is not recommended to exceed 90%.
Storing batteries in the optimal environment: Normally we recommend our customers to store lithium batteries at 0-33°C. Of course, the optimal environment is not only the temperature, but also the relative dryness and the humidity should be ≤ 60% ROH.
Use the charger brand provided by the manufacturer or specified for charging your lithium battery, to ensure that the voltage and current of the charger match your battery, and no overcharge or overdischarge will occur in the process of charging and discharging.
Prevent physical impact: Physical impact may cause the screws inside the battery to loosen or the welding points to dehiscence, which will cause the internal resistance of the battery to rise, and the temperature will be high during the use, affecting the life of the battery.
Regularly replenish lithium batteries: For lithium batteries that have not been used for a long time, we recommend that you replenish the battery’s charge every 3-6 months to prevent it from self-discharging and causing the battery to over-discharge.

Safety Tips
Some lithium batteries, such as lithium batteries for electric forklifts, work at higher voltages, when repairing, be sure to confirm that the battery’s power supply has been turned off, to avoid direct contact with the battery’s positive and negative terminals, improper operation may receive a click, need to wear insulated gloves.
If the temperature of the lithium battery is too high, please first give the lithium battery physical cooling or wait for it to cool down naturally, the heat is too high will lead to internal short-circuit of the battery, triggering a fire or explosion.
The inside of lithium battery usually consists of multiple single cells in series or parallel, so you need to fully communicate and learn with the manufacturer or supplier in advance when repairing, and it is best to complete all the repair work under the guidance of the manufacturer.
When the lithium battery is damaged, it may produce toxic gas or powder, which needs to be repaired under safety protection to avoid direct contact or inhalation.
Conclusion
After reading this post, I believe you have a very clear idea of the steps to follow on how to quickly start a dead lithium battery, and mastering this skill is invaluable. However, please note that all the steps need to follow the manufacturer’s requirements or operate under the premise of ensuring safety, insulated gloves, protective eyewear, flame-retardant coveralls, and fire extinguishers are all very important equipment to have on hand.
If you have followed our instructions but your lithium battery still does not work properly, then you need to seek more professional help or replace the lithium battery. BSLBATT as a professional lithium battery manufacturer, we have a lot of professional lithium battery engineers, if you have any questions, you can contact us at any time.