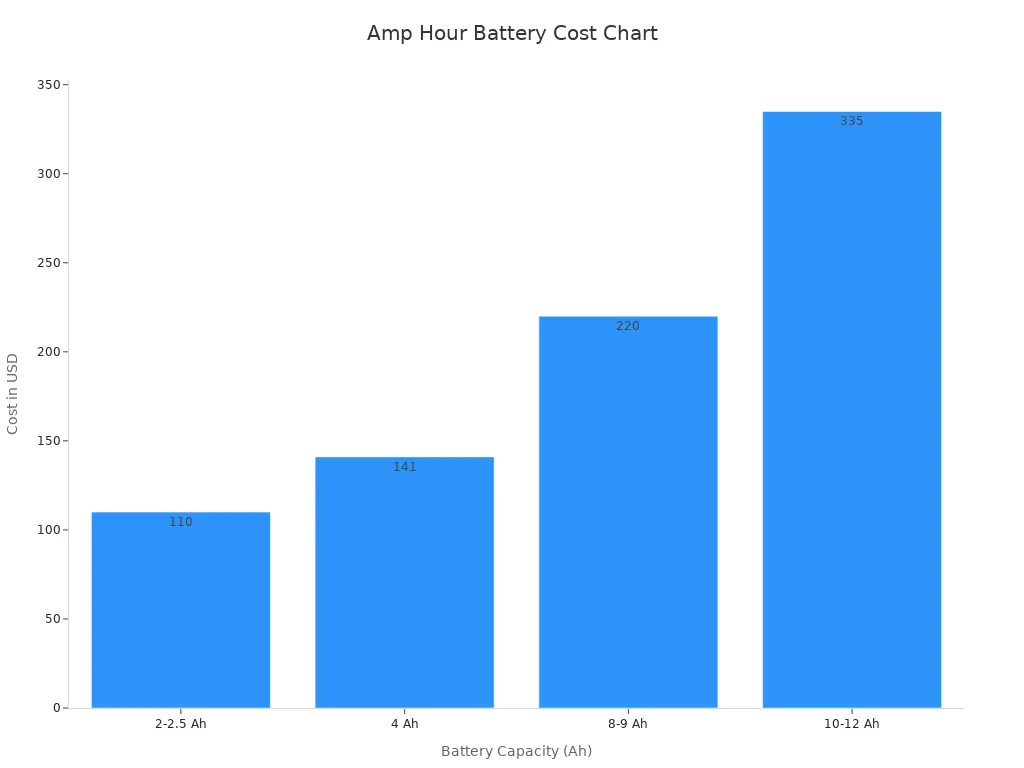
The lithium battery price in 2025 averages about $151 per kWh. Electric vehicle lithium battery packs cost between $4,760 and $19,200. Outdoor power tools and forklift lithium battery costs depend on amp hours, ranging from $110 for 2 Ah models to $335 for 12 Ah. Solar and energy storage system batteries show similar trends. The table below provides a detailed breakdown:
Application / Metric | Cost Range / Value |
|---|---|
Average lithium battery cost per kWh | Approximately $151 per kWh |
Electric Vehicle Battery Cost Range | $4,760 to $19,200 per battery |
2 to 2.5 Ah (Industrial/Tools) | Around $110 |
4 Ah | Around $141 |
8 to 9 Ah | Around $220 |
10 to 12 Ah | Around $335 |
Battery Lifespan (Charge Cycles) | 1,000 to 3,000 cycles |
Typical Lifespan in EVs/Storage | Up to 10 years |
Prices in 2025 continue a downward trend from previous years, making lithium batteries more affordable. Lower costs help buyers in sectors like transportation, renewable energy, and logistics.
Lithium Battery Price Overview
2025 Average Price per kWh
In 2025, the average lithium battery price per kilowatt-hour (kWh) continues to fall. Most industry forecasts place the global average between $85 and $100 per kWh, with some sources projecting even lower prices in high-volume markets. For example, battery packs in China now cost as little as $94 per kWh, while prices in the United States and Europe remain higher by 31% and 48% respectively. This steady decline reflects advances in manufacturing, increased production capacity, and lower raw material costs.
Year | Average Lithium Battery Price per kWh (USD) | EV Battery Price (USD/kWh) | BESS Price (USD/kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
2010 | Approx. $1000+ | N/A | N/A |
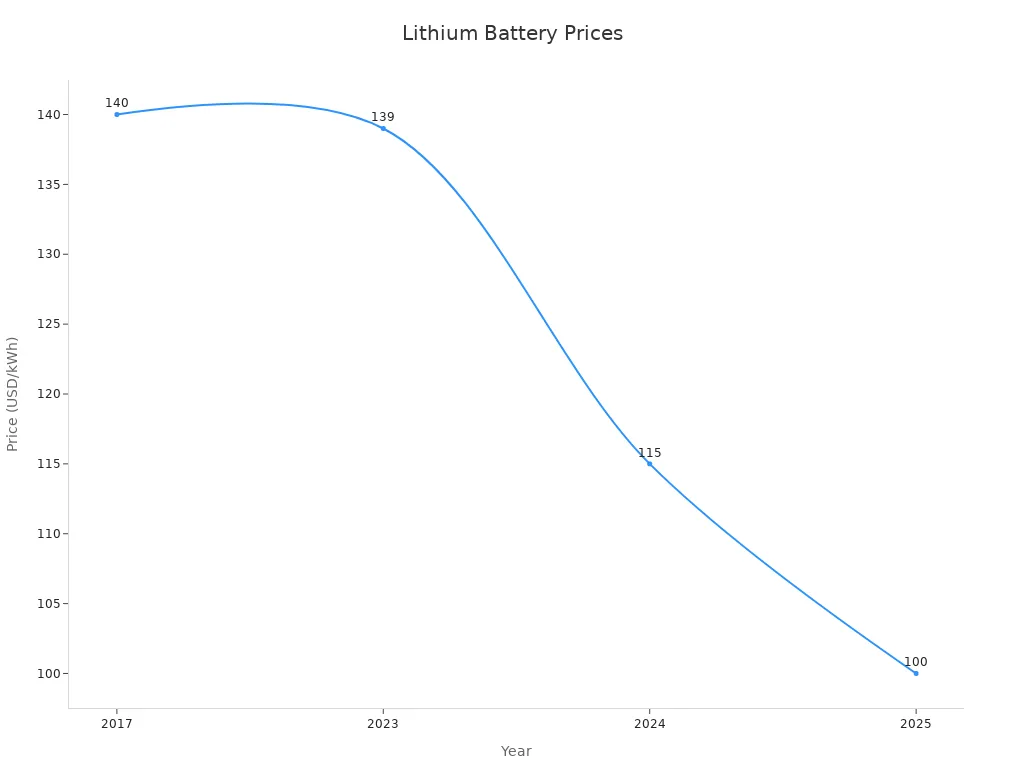
2017 | $140 | N/A | N/A |
2023 | $139 | Below $100 | N/A |
2024 | $115 | Below $97 | $125 |
2025 | Projected $100 or slightly below | Below $100 (expected) | N/A |
Note: The 2024 price drop of 20% marked the steepest annual decline in recent years.
Price by Application
Lithium battery prices vary by application. Electric vehicle (EV) battery packs in 2025 typically range from $4,760 to $19,200 per pack, depending on size and manufacturer. For solar and stationary energy storage systems, battery packs cost between $6,000 and $12,000. Leading brands like Tesla and Toyota offer battery packs within these ranges, with Tesla’s Powerwall and Megapack products reflecting the latest price trends. Industrial and material handling batteries, such as those used in forklifts, show similar cost patterns, with prices scaling according to capacity.
Application / Metric | Cost Range / Value |
|---|---|
EV Battery Pack | $4,760 – $19,200 |
Solar/Stationary Storage | $6,000 – $12,000 |
2 to 2.5 Ah (Industrial/Tools) | Around $110 |
10 to 12 Ah | Around $335 |
Yearly Price Trend
The lithium battery price has dropped sharply over the past several years. In 2023, the average price per kWh stood at $139. By 2024, it fell to $115—a 20% year-over-year decline, the largest since 2017. This trend continued into 2025, with prices projected to reach or dip below $100 per kWh. The main drivers include a surplus of battery materials, lower costs for lithium and cobalt, and fierce competition among manufacturers, especially in China.
Battery material prices also dropped significantly. For example, lithium carbonate prices fell from about $70,000 per metric ton in 2022 to less than $15,000 in 2024. Cobalt prices dropped by more than half in the same period. These reductions have made lithium batteries more affordable for both consumers and businesses.
Price Drivers
Raw Materials
Raw materials play a major role in lithium battery pricing. Lithium, cobalt, and nickel are the most important components. Their prices often change due to supply and demand. In recent years, lithium prices have dropped sharply. This happened because more companies started mining lithium and demand slowed down. BloombergNEF reports that battery pack prices closely follow raw material costs. In 2023, battery packs for electric vehicles averaged $128 per kWh, while the cells alone cost $89 per kWh. Cells make up about 78% of the total pack cost. China leads with the lowest battery prices, while the United States and Europe pay more due to higher production costs and less mature markets.
Market volatility affects these prices. Fastmarkets notes that supply chains for lithium and other battery materials often face imbalances. Prices can swing quickly when supply or demand changes. The MarketsandMarkets report points out that limited availability and concentration of these materials can cause bottlenecks. Geopolitical tensions and new mining regions, such as Latin America and Africa, also influence costs. When raw material prices drop, battery prices usually fall as well. This direct link makes raw materials a key driver in the lithium battery market.
Manufacturing Advances
Manufacturing improvements have helped lower lithium battery prices. Factories now use better technology and automation. This allows them to produce batteries faster and with fewer errors. The Bureau of Economic Analysis shows that from 2020 to 2023, domestic energy storage battery manufacturing output grew by 57.6%. This growth means more batteries enter the market, which helps push prices down.
Industry reports show a shift from older lead-acid batteries to modern lithium-ion batteries. This change happened during the 2010s as companies invested in new equipment and processes. As a result, battery quality improved and costs dropped. Chinese manufacturers lead the world in battery production. Their lower labor and energy costs, along with advanced manufacturing, give them a price advantage. These advances help explain why battery prices keep falling each year.
Policy Impact
Government policies shape the lithium battery market. Subsidies, tariffs, and new laws can all affect prices. The United States, for example, passed the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act and the Inflation Reduction Act. These laws provide subsidies for domestic battery production. They also add tariffs to imported batteries, making local products more competitive.
Trade statistics from the U.S. Census Bureau show changes in battery imports and exports since 2012. In 2024, U.S. lithium-ion battery prices were about 90% higher than Chinese imports before subsidies and tariffs. Policies like these help offset higher domestic production costs. They also encourage companies to build more factories in the United States and Europe. However, these efforts can raise prices in the short term due to higher energy and labor costs. Over time, strong policy support can help lower prices by boosting local supply and competition.
Industry reports show a shift from older lead-acid batteries to modern lithium-ion batteries. This change happened during the 2010s as companies invested in new equipment and processes. As a result, battery quality improved and costs dropped. Chinese manufacturers lead the world in battery production. Their lower labor and energy costs, along with advanced manufacturing, give them a price advantage. These advances help explain why battery prices keep falling each year.
Note: Policy changes, manufacturing advances, and raw material trends all work together to shape lithium battery prices. Buyers should watch these factors to understand future price movements.
Application Breakdown
EVs
Electric vehicles (EVs) rely on lithium-ion batteries for power and range. Over the past few years, the lithium battery price for EVs has dropped by 20-50%. This sharp decline has encouraged many manufacturers to move production to countries like China, where costs are lower. Specialty batteries made in the United States and Europe, often used for defense or industrial purposes, remain more expensive than mass-produced batteries from Asia.
Automakers have increased the battery capacity in new EV models. However, fixed effects regression analysis shows that EV prices have risen more than the actual increase in battery costs. This means that car companies may charge buyers more than the savings from lower battery prices. The result is a price variation in lithium batteries by application, especially in EVs, where the cost reduction does not always reach the consumer.
EV battery prices have dropped sharply as production shifts to lower-cost regions, but consumers may not fully benefit from these reductions.
Solar Storage
Solar storage systems use lithium-ion batteries to store energy from solar panels. The price of these batteries has fallen by about 97% since 1991, dropping from $7,500 per kWh to $181 per kWh by 2018. This trend matches the overall market, including EVs and portable electronics. Between 2014 and 2018, prices for lithium batteries used in solar storage halved, thanks to better technology and larger production volumes.
In solar home systems, lithium-ion batteries cost more upfront than lead-acid batteries. For example, a 170 Wh lithium-ion battery costs around $160, while a similar lead-acid battery costs about $45. Despite the higher initial cost, lithium-ion batteries offer a lower total energy cost—about 25% less—because they last longer and perform better. In 2020, a 2.5 kWh lithium-ion battery pack for a solar home system cost about $1,190, with the cells making up nearly 60% of that price. The solar storage market often uses battery cells originally made for EVs, which affects both availability and pricing. As EV demand grows, the learning rate for lithium-ion batteries remains high, leading to annual cost reductions of about 4%.
Tip: Homeowners who invest in lithium-ion solar storage may pay more upfront but save money over time due to longer battery life and better efficiency.
Consumer Electronics
Consumer electronics, such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets, depend on small lithium-ion batteries. These devices benefit from the same price trends seen in larger applications. As battery technology improves and production scales up, the cost of batteries for consumer electronics continues to fall. Manufacturers can now offer longer battery life and faster charging at a lower cost.
The lithium battery price for consumer electronics has become more affordable each year. This trend allows companies to add new features without raising prices. Consumers enjoy better performance and reliability in their everyday devices.
Advantages for consumers:
- Lower device prices
- Longer battery life
- Improved safety and reliability
Material Handling
Material handling covers equipment like forklifts, pallet jacks, warehouse robots, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs). These machines move goods in factories, warehouses, and distribution centers. Lithium batteries have become the preferred power source for this equipment in 2025.
Companies choose lithium batteries for material handling because they offer several advantages over traditional lead-acid batteries. Lithium batteries charge faster and last longer. Workers can use equipment for more hours each day. Maintenance needs drop because lithium batteries do not require watering or equalizing. This saves time and reduces labor costs.
The price of lithium batteries for material handling equipment has followed the same downward trend seen in other sectors. In 2025, a typical lithium battery for a Class I or II forklift costs between $7,000 and $15,000, depending on capacity and brand. Smaller batteries for pallet jacks or AGVs range from $2,000 to $6,000. The table below shows common price ranges:
Equipment Type | Battery Capacity (kWh) | Price Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|
Forklift (Class I/II) | 14 – 40 | $7,000 – $15,000 |
Pallet Jack | 2 – 5 | $2,000 – $4,500 |
AGV/Robot | 3 – 10 | $3,000 – $6,000 |
Note: Prices depend on battery chemistry, brand, and warranty terms.
Lithium batteries help companies lower their total cost of ownership. They last up to five times longer than lead-acid batteries. Many lithium batteries provide 2,000 to 4,000 charge cycles. This means fewer replacements and less downtime. Fast charging allows for opportunity charging during breaks, so equipment stays in service longer.
Warehouse managers also value the safety features of lithium batteries. Most models include built-in battery management systems (BMS). These systems monitor temperature, voltage, and current. They help prevent overheating and extend battery life.
Key benefits of lithium batteries in material handling:
Longer lifespan and more charge cycles
Faster charging and less downtime
Lower maintenance costs
Improved safety with BMS technology
Companies that switch to lithium batteries often see a return on investment within two to four years. They spend less on maintenance and replacement batteries. Workers can operate equipment more efficiently.
Tip: Buyers should compare battery warranties, cycle life, and after-sales support before making a purchase. Choosing the right battery can maximize savings and boost productivity in material handling operations.
Regional Differences
Asia
Asia leads the world in lithium battery production and price competitiveness. China, South Korea, and Japan host many of the largest battery manufacturers. These countries benefit from advanced manufacturing, lower labor costs, and strong government support. In 2025, battery prices in Asia remain the lowest globally. For example, Chinese battery packs often cost 31% less than those in the United States.
Price trends in Asia show significant swings throughout the year. The first quarter of 2025 saw price changes driven by high electric vehicle (EV) demand, production slowdowns during the Chinese New Year, and oversupply. Regulatory changes also played a role. By the third quarter of 2024, oversupply and trade tensions led to a marked price drop. New battery chemistries and bearish market sentiment added to the volatility.
Quarter | Asia Pacific Price Trends and Drivers |
|---|---|
Price swings from EV demand, production disruptions, oversupply, and regulations | |
Q4 2024 | Volatility and stabilization; price climb from EV demand and government stimulus |
Q3 2024 | Marked price drop from oversupply, trade tensions, new chemistries |
Q2 2024 | Price rise from energy storage and EV interest; regulatory and logistical challenges |
Q1 2024 | Substantial price variations from oversupply and low demand |
Note: Asia’s battery market responds quickly to changes in supply, demand, and policy. Buyers in this region often see the fastest price adjustments.
Europe
Europe’s lithium battery market faces different challenges. Countries like Germany, France, and the United Kingdom invest heavily in battery production and EV adoption. However, Europe often pays higher prices than Asia due to higher labor costs and stricter regulations. In 2025, European battery prices reflect both local production costs and global supply chain issues.
Recent data shows that Europe experienced price increases in early 2025. Raw material production costs and policy changes affected the market. Falling new car registrations and mixed demand also influenced prices. In late 2024, oversupply and weak EV demand caused price drops and spikes. Supply chain strains added to the instability.
Quarter | Europe Price Trends and Drivers |
|---|---|
Q1 2025 | Price increase from raw material production; mixed demand; policy changes |
Q4 2024 | Instability from excess supply and weak EV demand; price drops and spikes |
Q3 2024 | Major price decreases from oversupply, weak demand, supply chain disruptions |
Q2 2024 | Price stability from supply management; slight demand decrease |
Q1 2024 | Price declines from low demand and excess supply; constrained market |
Europe’s market includes a wide range of battery types, such as NMC, LFP, and NCA. The region’s market size reached $109.9 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow to $221.7 billion by 2029. Growth comes from EV sales, energy storage demand, and government support for electrification.
North America
North America, including the United States, Canada, and Mexico, shows steady growth in lithium battery adoption. The region’s prices remain higher than Asia but often lower than Europe. In 2025, North American battery prices fluctuate due to EV demand, federal incentive changes, and supply chain adjustments.
The first quarter of 2025 brought price swings as EV demand rose and federal incentives changed. Restocking drops added to the volatility. In late 2024, tighter industry rules helped stabilize prices, and oversupply concerns eased. Earlier in 2024, low demand and excess supply caused severe price decreases.
Quarter | North America Price Trends and Drivers |
|---|---|
Q1 2025 | Fluctuating prices from EV demand, incentive uncertainties, restocking drops |
Q4 2024 | Price swings from supply-demand issues; recovery from tighter rules |
Q3 2024 | Considerable price drop from oversupply, supply chain issues, less government support |
Q2 2024 | Remarkable price stability with balanced supply-demand; strategic adaptations |
Q1 2024 | Severe price decrease from low demand and excess supply; pessimistic outlook |
North America’s market covers a broad range of battery chemistries and applications. Key drivers include EV adoption, energy storage needs, and government support. Major companies like Tesla, LG Energy Solution, and Panasonic operate in this region, shaping both prices and innovation.
Tip: Regional price differences depend on local production, supply chain stability, and government policies. Buyers should track these factors when planning battery purchases.
LFP vs. NMC Battery Chemistry
Lithium iron phosphate (LFP) and nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC) batteries dominate the lithium battery market in 2025. Each chemistry offers unique strengths and trade-offs. LFP batteries use a 3D lattice structure for lithium ion movement. This structure increases safety and extends cycle life. NMC batteries rely on 2D interlayers, which allow for higher energy density but can reduce stability.
LFP batteries avoid expensive and ethically sensitive materials like cobalt and nickel. This choice lowers costs and supports a more stable supply chain. Manufacturers in China have accelerated LFP adoption because of these advantages. In 2024, LFP cell prices in China dropped below $60 per kWh. Companies like BYD pushed prices even lower, reaching around $44 per kWh through large-scale production and vertical integration. This price drop narrows the gap between LFP and NMC, making LFP a strong choice for cost-sensitive markets.
NMC batteries provide higher energy density, reaching up to 240 Wh/kg compared to LFP’s 180 Wh/kg. This difference means NMC batteries can deliver longer driving ranges in electric vehicles. However, LFP batteries remain cost-effective for most daily driving needs. A recent study found a “tipping point” at about 373.5 miles of vehicle range. For trips below this range, LFP batteries offer better value. Most U.S. household trips fall well below this threshold, so LFP batteries suit typical daily use and shorter-range EVs.
Feature | LFP Batteries | NMC Batteries |
|---|---|---|
Energy Density | Lower (180 Wh/kg) | Higher (240 Wh/kg) |
Cost | Lower | Higher |
Safety | Higher | Moderate |
Cycle Life | Longer | Shorter |
Supply Chain Stability | Strong | Sensitive to cobalt/nickel prices |
Best Use | Daily driving, solar | Long-range EVs, premium electronics |
Long-Term Market Outlook
Looking beyond 2025, most forecasts predict that lithium battery prices will continue to fall. The RMI report suggests that by 2030, lithium-ion battery costs could drop to between $32 and $54 per kWh. At the same time, energy density may improve to 600–800 Wh/kg. Battery sales are expected to rise sharply, reaching between 5.5 and 8 terawatt-hours each year. These changes will come from better technology, strong policy support, and fierce competition among manufacturers.
Regional trends also shape the long-term outlook. The table below summarizes key market dynamics and forecasts for different regions:
Region | 2023-2025 Trends | 2025-2033 Forecast |
|---|---|---|
Latin America | Oversupply, weak EV demand, high production, project delays eased oversupply | Market to grow from $5.70B (2024) to $7.83B (2033) at 3.42% CAGR |
North America | Oversupply, low demand, production cuts, export moderation stabilized prices | Cautious procurement, price volatility to moderate |
Asia Pacific | Oversupply, price drops, production adjustments, modest demand recovery in EV and storage sectors | Prices to stabilize as EV and ESS demand grows |
Middle East & Africa | Industrial growth, resource availability, geopolitical tensions influence prices | Regional factors to keep shaping price dynamics |
Several factors will drive market growth over the next decade. Recycling programs, smart technology integration, and product customization will boost demand and innovation. The fastest-growing segment will be energy storage systems, fueled by the need for sustainable energy and new technology. North America will benefit from EV incentives, Europe will push green technology, and Asia-Pacific will expand production capacity. Latin America and the Middle East will emerge as important new markets.
Lithium Battery Buying Guide
Total Cost of Ownership
When buyers consider lithium batteries, they should look beyond the sticker price. The total cost of ownership (TCO) includes all expenses over the battery’s life. Many factors affect TCO:
The average lithium ion battery costs about $151 per kWh, but prices keep dropping as technology improves.
Lithium batteries last much longer than lead-acid batteries, often reaching 1,000 to 3,000 charge cycles. Lead-acid batteries usually last only 500 to 1,000 cycles.
Maintenance costs are lower for lithium batteries. Most come with warranties of 5 to 10 years, reducing the risk of early replacement.
Recycling costs for lithium batteries are higher, but their longer lifespan and environmental benefits help balance this out.
LiFePO4 batteries, a type of lithium battery, need no maintenance during their lifetime. Lead-acid batteries require regular water topping, cleaning, and corrosion checks.
Charging costs are lower for lithium batteries because they charge more efficiently and waste less energy.
Despite higher upfront costs, save money over time. They need fewer replacements, have lower maintenance, and use energy more efficiently. Electric vehicles with lithium batteries also cost less to run than those with internal combustion engines. Buyers should add up all costs—purchase, installation, maintenance, charging, and recycling—to see the real value of a lithium battery.
Brand Comparison
Brand choice affects both price and performance. Leading brands like Tesla, BYD, LG Energy Solution, and BSLBATT offer different strengths.
Buyers should look at warranty terms, after-sales support, and product reviews. Some brands focus on high performance, while others offer better value for money. Matching brand strengths to specific needs ensures the best outcome.
Brand | Strengths | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
Tesla | High energy density, smart tech | EVs, home storage |
BYD | Low cost, strong LFP options | EVs, buses, solar storage |
LG Energy | Reliable, global support | EVs, electronics |
Custom solutions, safety focus | Material handling, solar |