Globally, batteries are playing an increasingly important role in everyday life. Countless devices rely on these little energy packs to function, from TV remotes and alarm clocks to flashlights and mini-fans. Of the many types of batteries available, alkaline and lithium batteries are undoubtedly two of the most common on the market. But have you ever thought deeply about the difference between the two? If you needed to choose a battery for a particular device, how would you decide whether to use alkaline or lithium batteries?
In this article, we’ll take an in-depth look at how alkaline and lithium batteries work, explore their strengths and weaknesses, and how they perform in real-world applications. Whether you’re a manufacturer of electronic devices or just a casual consumer curious about batteries, we hope that this article will help you understand the differences between these two common battery types more clearly.
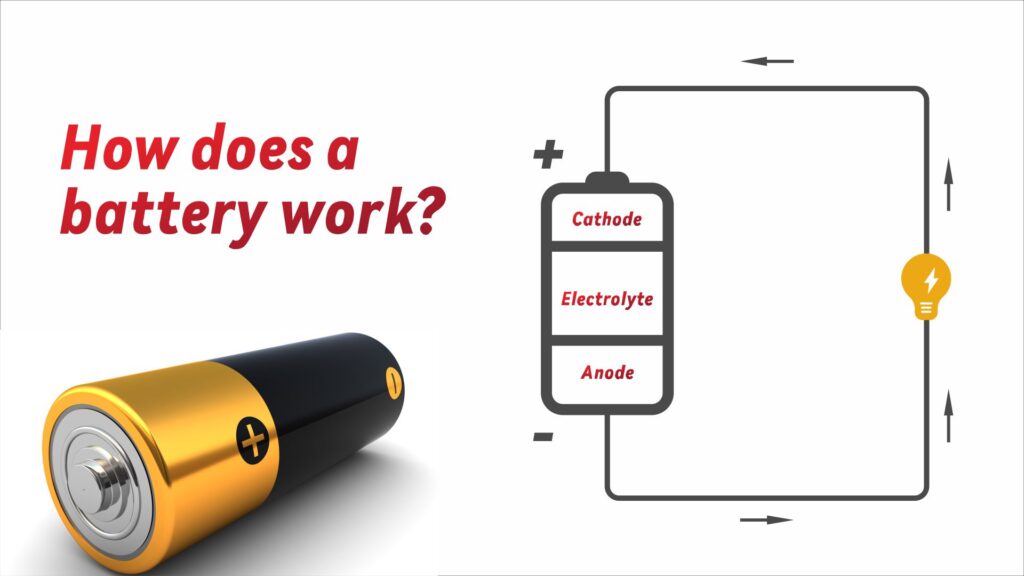
Understanding How Batteries Work
Before we can explore the difference between alkaline and lithium batteries, we first need to understand how batteries work and the various types they come in. Batteries, simply put, are devices that store energy. They store chemical energy and convert it into electrical energy for use in various devices such as golf carts, electric forklifts, boats, AGVs and various other devices.
Click here to learn: What Are Lithium Batteries Used For?
The working principle of a battery relies heavily on two different chemicals and the chemical reaction between these two substances results in the flow of an electrical charge. These chemicals are usually placed on two separate electrodes of the battery, one known as the anode and the other as the cathode. The charge flows from the anode to the cathode, passing through a substance called an electrolyte in between, and this is the process we call ‘discharge’. It is in this way that the energy of the battery is released.
There is a wide range of batteries available in the market, the most common of which are undoubtedly alkaline and lithium batteries. To understand the characteristics and performance of these two types of batteries, it is important to start with their construction and working principles. In the next section, we will delve into the details of alkaline batteries and lithium batteries to understand the differences between them.

Alkaline Batteries
- How Alkaline Batteries Work
Alkaline batteries work based on a chemical reaction between the cathode and anode. When an alkaline battery is connected to an electrical circuit, electrons flow from the cathode (negative) to the anode (positive), through an external circuit, and then back to the cathode of the alkaline battery. As the electrons leave the cathode, they leave behind ions (e.g., Zn2+) that pass along the electrolyte to the anode. At the anode (positive), the ions accept electrons (typically from MnO2) and are converted to new substances (e.g., Zn(OH)2), which combine with potassium hydroxide (the electrolyte) and form new ions.
- Main Applications of Alkaline Batteries
Alkaline batteries are a common type of household and industrial power source that is widely used in numerous devices in our daily lives. What makes these batteries unique is that they excel in a variety of devices that require long-lasting performance and frequent use.
Alkaline batteries are often preferred as the first choice in a variety of household electronics. Such as flashlights, remote controls, calculators, and alarm clocks, these types of devices consume relatively low amounts of energy, and alkaline batteries as a power source can provide long-lasting power support.
In addition to this, alkaline batteries are also used in a large number of applications in some industrial fields. Some of the more common examples include circuit boards, metering equipment, thermometers, logistics machinery, etc.; in medical equipment, like hearing test equipment, blood glucose testers, etc. often.
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Alkaline Batteries
Through years of technological development and accumulated experience in use, alkaline batteries have demonstrated their solid position in the market. However, like all products, they have their own advantages and disadvantages.
Pros:
First of all, alkaline batteries have a relatively high energy density, which allows them to supply power for a fairly long period, especially in some lower power applications such as remote controls and flashlights. In addition, alkaline batteries have a relatively flat discharge curve, meaning they can provide a relatively stable voltage over most of their life cycle. And, their structural design allows them to maintain good performance even when not in use for extended periods.
Second, alkaline batteries are very cost effective. They are relatively inexpensive to produce and are in plentiful supply in the marketplace, which makes them readily available to you almost anywhere.
Finally, not to be overlooked, alkaline batteries are environmentally friendly. Under regular use, alkaline batteries perform consistently and do not leak liquids or gases. And compared to many other types of batteries, alkaline batteries can be recycled and disposed of to a large extent, drastically reducing their impact on the environment.
Cons:
However, alkaline batteries are not perfect, and they do have significant drawbacks. First, alkaline batteries are not rechargeable. Once they are depleted, we have no choice but to replace them, and they cannot be recharged for reuse. This undoubtedly adds to the ongoing cost of using battery-operated devices.
Second, while alkaline batteries have a higher energy density, they discharge faster than some more advanced battery technologies such as lithium batteries, especially in devices that require high volume discharges, and performance may degrade over long periods with high current discharges.
In addition, due to the presence of harmful chemicals such as potassium hydroxide and manganese dioxide, alkaline batteries need to be properly sorted and disposed of after use to avoid environmental contamination.
Finally, alkaline batteries can experience performance degradation under extreme environmental conditions, such as very high or very low temperatures. This also limits their use in certain more demanding applications.

Lithium Batteries
About what is lithium batteries, we have done a detailed introduction in the previous article, interested in reading this article, to get a more detailed knowledge of lithium batteries.
- How Lithium Batteries Work
Like most batteries work, lithium batteries are divided into a cathode and an anode. Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable batteries that utilize a compound containing Li+ ions as the positive electrode.
The working principle of lithium batteries relies mainly on the movement of lithium ions between the positive and negative electrodes. In the charging state, Li+ moves from the positive electrode to the negative electrode through the electrolyte and is embedded in the negative electrode material, a process that results in electrical energy. In the discharged state, these Li+ embedded in the negative electrode will be released and return to the positive electrode through the electrolyte, while releasing electrical energy.
- Main Applications of Lithium Batteries
Lithium batteries are also widely used, based on their safe, environmentally friendly and high energy density characteristics, and are relied upon in smartphones, laptops, and rechargeable devices such as tablets and wireless headsets.
Secondly, lithium batteries are also used in many applications in the power field, such as electric forklifts, golf carts, ships, AGVs and other industrial equipment, which is mainly attributed to the lithium battery’s maintenance-free, fast-charging, excellent power conversion efficiency and long-lasting power supply, which can reduce the employer’s operating and working costs, and enhance the economic benefits.

Finally, lithium batteries also have very important applications in the renewable energy transition. By storing power from wind, solar and other clean energy sources, on the consumer side, they can save power costs or have a reliable backup power source in case of grid outages; on the power generation side, they can help smooth out peaks in the grid, reduce loads and ensure power stability.
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Lithium Batteries
The development of lithium batteries has only a few decades, but has become an important power energy equipment in modern society, mainly because for traditional batteries, lithium batteries have many unique advantages, but there are also some disadvantages.
Pros:
The first thing that should be mentioned is the high energy density of lithium batteries. Because lithium is the lightest metal and has high electrochemical activity, this makes lithium batteries have a higher energy density than other types of batteries, which can provide longer-lasting power for electronic devices and industrial applications under the same volume or weight.
Second, Li-ion batteries have a low self-discharge rate, which means that they do not lose too much power even when they are not used for a long period, making them suitable for use as a power source for some long-term standby or low-current devices.
In addition, Li-ion batteries are safe and environmentally friendly, with no acid, and will not harm the environment or the human body.
Li-ion batteries can be monitored by BMS, which can provide a variety of protection, such as high temperature, over-voltage, over-current, etc., which can prolong the service life of the battery.
Finally, lithium batteries have a higher charging efficiency and longevity than many other types of rechargeable batteries. Typical lithium batteries can reach thousands of charge/discharge cycles, which means they last longer, require less time to recharge, and save money by replacing batteries less frequently.
Cons:
However, lithium batteries also have some drawbacks. The most important is safety. Due to the highly reactive nature of lithium, lithium batteries can trigger a thermal runaway reaction under overcharging, over discharging, or another improper handling, causing the battery to heat up and even produce toxic fumes, flames, or explosions.
Key Differences Between Alkaline And Lithium Batteries
Lithium batteries and alkaline batteries are both indispensable sources of energy in everyday life. They have a variety of uses in daily life, electronic devices and industrial applications, but they differ very much in terms of material, price, voltage, capacity, cycle life and application.
Materials
In alkaline batteries, zinc and potassium hydroxide are usually used as electrolytes. The positive electrode material is usually a manganese oxide, such as manganese dioxide. The negative electrode material is mostly zinc powder. The main chemical reaction that takes place in an alkaline battery is the reaction of zinc with manganese dioxide in a potassium hydroxide solution to produce electrical energy.
In lithium batteries, lithium is used as the electrolyte, often with lithium-containing compounds such as lithium salts. The positive and negative electrode materials of lithium batteries can have a variety of choices, which is the reason why there are so many different types of lithium batteries.
For example, in lithium ion batteries, the positive electrode material is mostly lithium nickel cobalt oxide (NiCoAl), lithium iron phosphate, etc., and the negative electrode is graphene; and in lithium polymer batteries, the positive electrode material is also often lithium nickel cobalt oxide or lithium iron phosphate, and the negative electrode material is lithium metal.
Price
Alkaline batteries are cheaper than lithium batteries due to their relatively simple materials and production process, and their lower cost. Lithium batteries, on the other hand, are more expensive due to the higher-end materials and production technology used.
Voltage
Alkaline batteries typically have a voltage of 1.5 volts, while a typical lithium battery has a voltage of 3.6 volts. Lithium batteries have a higher voltage, which makes them better able to function in high-performance devices.
Capacity
The energy density of lithium batteries allows them to store more power in the same volume. This allows lithium batteries to have wider use in applications that require dense energy output, such as smartphones and electric vehicles.
Cycle Life
Alkaline batteries are disposable, cannot be recharged and need to be replaced after use. Lithium batteries can be recharged and used repeatedly, and a typical lithium battery can support more than 3,000 charge/discharge cycles (depending on the product application).
Applications
The main difference between alkaline batteries and lithium batteries in application scenarios lies in the power requirements of the device, cost and size. For example, according to their product characteristics, alkaline batteries are often used in some low-power consumption devices, such as alarm clocks and remote controls. Lithium batteries, on the other hand, are widely used in high-power consumption devices such as cell phones, laptops, photographic equipment and electric vehicles.
Performance
The main performance differences between the two are energy density, voltage and cycle life. Lithium batteries have a higher energy density, can provide higher voltage and are rechargeable. Alkaline batteries, while less expensive, may have a higher total cost for long-term use because they are not rechargeable.
How to Choose The Type of Battery For Specific Needs?
Although batteries can be found everywhere, when faced with various battery types such as alkaline batteries and lithium batteries, how should we choose the most suitable one?
Identify your device’s needs
First of all, you need to be clear about what exactly your device needs. This includes the device’s voltage needs, the device’s power needs, the environment in which the battery is used, and how often the device is used. For example, digital products such as smartphones, cameras, etc. usually require a higher voltage and long-lasting use time, while frequent charging is more suitable for lithium batteries. For remote controls, alarm clocks and other devices that use less power, alkaline batteries are a good choice.
Cost is also a big factor to consider
Devices that require battery replacement at every turn, such as toys and alarm clocks, are more suited to the use of low-cost and safer alkaline batteries. And because lithium batteries have a longer lifespan and strong rechargeability, for devices like cell phones and laptops that are heavily used, despite the higher initial acquisition cost, lithium batteries offer better value for money in the long run.
Where to Find The Best Lithium Battery Manufacturers?

BSLBATT is a professional Lithium battery manufacturer located in Guangdong, China, where there are many famous Li-ion battery manufacturers such as EVE, BYD, etc. BSLBATT means Best Lithium Battery Solution, we have a team of engineers with more than 10 years of lithium Battery experience who can provide lithium Battery products and solutions for many scenarios for our customers, including Power Forklifts, Golf Cart Batteries, etc. BSLBATT is the best lithium battery solution for our customers.